Individual Project 1 Due Wednesday September 18, 2024 12:00pm EST (Noon)
Welcome aboard to the Stack Overflow team! We’re glad that you’re here and ready to join our development team as a new software engineer. We’re building an interactive application for an online community to share their knowledge and experience, and are very happy to see that we have so many new developers who can help make this application a reality. By the end of the semester, you’ll be able to propose, design, implement, and test new features for our project. We understand that some of you may have some web development experience, but don’t expect that most of you do, and hence, we have created an individual project to help you get up to speed with our existing codebase and development environment.
FakeStackOverFlow is a web application that consists of some code that runs in each client’s web browser, and also code that runs on a server.
This implementation effort will be split across two deliverables. In this first deliverable, you will implement and test the core backend components for this feature, and in the second deliverable, you will implement and test the frontend components.
Change Log
- 9/6/2024: Added clarification to files required to modify in Task 1
- 9/6/2024: Added clarification/instruction for
getTagByNamein Task 2 - 9/7/2024: Moved tutorial on MongoDB and Mongoose to tutorials
- 9/9/2024: With reference to Piazza post @38: Update handout to fix mocking request body used with ‘supertest’ in
newQuestion.spec.ts. Involves changes at 4 places: in line 86, replacesend(mockQuestion)withsend({ ...mockQuestion, title: '' }); in line 95, replacesend(mockQuestion)withsend({ ...mockQuestion, text: '' }); in line 104, replacesend(mockQuestion)withsend({ ...mockQuestion, tags: [] }); in line 113, replacesend(mockQuestion)withsend({ ...mockQuestion, asked_by: '' }); - 9/12/2024: Updated typo regarding file to test for Task 1. Tests are to be added in
questions.spec.tsinstead ofquestion.spec.ts - 9/18/2024: Updated typo in Task 3.
sortQuestionsByMostViewedis the function to be added (NOTgetMostViewedQuestion).
Objectives of this assignment
The objectives of this assignment are to:
- Get you familiar with the basics of TypeScript, VSCode, and the project codebase
- Learn how to read and write code in TypeScript
- Translate high-level requirements into code
- Learn how to write unit tests with Jest
Getting started with this assignment
Start by accepting our invitation. It will create a Github repository for you which will include the starter code for this assignment. In case you have enrolled in the course recently (after 9/3), you may not find your name in the list. Please create a piazza post to contact us and we will add you to the Github Classroom roster.
If you are new to Git, you may want to review this getting started page first!
1. Prerequisites
1.1 Install Node.js and npm
If you haven’t installed npm and node.js, follow the tutorial on setting up a development environment for this class
1.2 Install MongoDB
We use MongoDB as the NoSQL database to store data related to this application.
- Follow the instructions in the official MongoDB documentation to install the free community edition.
- Choose ‘Install on Linux’, ‘Install on macOS’, or ‘Install on Windows’, depending on your system. (the following steps are for Windows)
- Scroll down to the section labeled ‘Install MongoDB Community Edition.’ and click on MongoDB Download Center.
- For Windows, in the Package dropdown, select
msi. Then download and run the installer. - On Windows, select the “Install MongoDB as a Service” checkbox and install. This will start MongoDB as a background service.
- Install “MongoDB Compass” if prompted.
- Verify if the MongoDB server is running using the Windows Services app.
Mongo offers several methods of interacting with your Mongo databases.
-
MongoDB Compass is an interactive application for creating, modifying, and querying MongoDB connections. It should be started as part of the installation process, showing a connection to
mongodb://localhost:27017/.For Windows, install MongoDB Compass using the instructions above.
For Mac:
- Download the dmg file from https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/compass. Once the application starts:
- Click on “Add new connection” in the left sidebar.
- Make sure the URI field contains
mongodb://localhost:27017 - Click on “Connect” - MongoDB will need to be running as a macOS service
- Download the dmg file from https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/compass. Once the application starts:
-
Mongo shell (mongosh) provides a command-line interface that can be used to interact with databases in MongoDB.
For Windows:
- Download it here using the msi package. You can also use mongosh to see if the MongoDB server is running. Try the MongoDB Community Edition and the command
show dbs; you should see a list of existing databases in your local instance.
For Mac:
- Mongo shell is automatically installed with MongoDB through the Mac installation instructions. To use it, make sure MongoDB is running as a macOS service, then type
mongoshinto the terminal.
- Download it here using the msi package. You can also use mongosh to see if the MongoDB server is running. Try the MongoDB Community Edition and the command
-
Last and most important, you can use the Mongoose api to interact with MongoDB through your JavaScript or TypeScript programs. Mongoose will be installed as part of the installation process for the project starter code.
2. Install the starter code and its dependencies
The starter code package, of which this is a part, is divided into 3 main directories: client, server, and testing.
- Navigate to the root directory of the repo.
- Install the dependencies for each directory by running the following commands:
cd client/
npm install
cd ../server
npm install
cd ../testing
npm install
Once you install the dependencies, you might see the following ESlint errors in some files. The linter error indicates that the code contains carriage return characters (\r, represented as ␍) at the end of each line and usually happens when the file has Windows-style line endings (\r\n) instead of Unix-style line endings (\n). To fix this, you can click on the “CRLF” icon on the lower right corner of VSCode and change it to “LF”. Note that this does not count as a linting error when grading.
3. Populate the initial database
- In the
serverdirectory, runnpx ts-node populate_db.ts mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/fake_soto populate thefake_sodatabase with data that follows the schema definition.
Note: Right now, you may run into errors regarding unknown properties. Once you finish implementing Task 2 and Task 4 and modify the schema, you should be able to populate the database correctly.
4. Familiarize Yourself with Project Dependencies
- Ensure the following packages are installed: mongoose, express, jest, eslint, axios, cors, and nodemon.
- Refer to the documentation for the following packages:
-
Express is a framework to write server-side code.
- The mongoose data modeling library. Mongoose provides JS/TS bindings to MongoDB, so we can manage and manipulate the data from our JS/TS programs.
- nodemon accelerates the development by automatically restarting a node application when file changes in the directory are detected.
-
We use the axios library to send HTTP requests to our server from our client application.
-
We use cors to regulate the permissible connections between the clients and the server. The current cors configuration allows all connections to the server for convenience. This is fine for a development environment. In a production environment where the application is deployed on a cloud service, the CORS policy needs to be specified more strictly. Read more about CORS https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS.
- We use mockingoose to mock Mongoose functions when testing.
5. Explore Useful Resources
- Express Tutorial: https://expressjs.com/en/guide/routing.html
- MongoDB tutorial: A mini tutorial.
- Mongoose Queries: https://mongoosejs.com/docs/queries.html
- Mongoose Documents: https://mongoosejs.com/docs/documents.html
- Jest Basics: https://jestjs.io/docs/getting-started
- Mocking in Jest: https://jestjs.io/docs/mock-functions
- Mocking Mongoose functions: https://github.com/alonronin/mockingoose
Server/Client Architecture
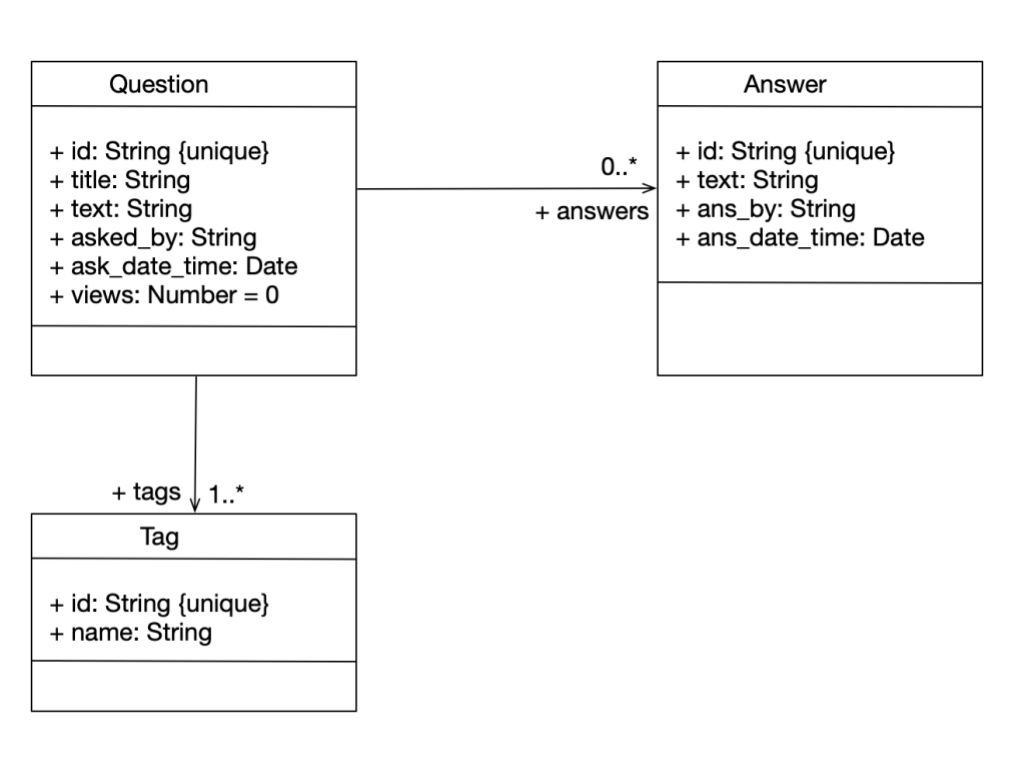
The schemas for the database are documented in the directory server/models/schema.
A class diagram for the schema definition is
shown below:
The starter code package, of which this is a part, is divided into 3 main directories: client, server, and testing.
Client
Running npm run start will start a client on port 3000.
The client code uses Axios to send HTTP method requests to the server. You should review the client code to understand
how axios sends requests and how the response from the server is processed. You don’t need to make any changes to the client code.
Server
The server is responsible for taking HTTP requests from the client and executing them on the database. The server code resides in the server/ directory. The server is responsible for all the data that is sent back and forth to the database.
The main server script is in server/server.ts. Running npx ts-node server/server.ts
will start an HTTP server, which will take HTTP requests on https://localhost:8000, and execute them on the running database instance.
You can send requests to the server using a tool like Postman, or by writing scripts that use axios to send requests to localhost:8000, as you did in the Async activity.
When the server is terminated (using CTRL+C), the message “Server closed.” should be displayed. However, the MongoDB service will still be running (You can run mongosh to confirm)
Testing
Unit tests for the server are in server/tests/*.spec.ts. These are written in Jest, which you are already familiar with.
To run the entire set of server tests, go to the server directory and say npm run test. Please ensure that the MongoDB server is up and running for the tests to pass.
If you want to run specific tests, we recommend that you install vsc-jest-runner in your VSC, and select the test or tests that you would like to run.
Summary of the default host/port settings
| Client Instance | https://localhost:3000/ |
| Server Instance | https://localhost:8000/ |
| Database Instance | mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/fake_so |
Recommendations when working on the project
- Open the client application in a browser and interact with it. While interacting, monitor the application tab in the browser’s developer tools. The application tab will give you information about the HTTP requests the client sends to the server. The HTTP requests will contain URIs in their headers. You can use this information to understand the endpoints in the server.
- Read the Jest tests. The Jest tests list all the endpoints the server should have, and the types of HTTP method associated with them. Further, the tests also have information about the Mongoose functions that need to be invoked for the service to send a successful response.
- Start by defining the schemas in the server/models/schema directory to ensure the data structure is consistent.
- Ensure that you run all Jest tests. These tests are designed to catch issues early. Once all Jest tests pass, the Cypress tests should also pass, assuming no significant changes have been made to the client’s implementation.
- Follow the debugging policy to help in the debugging process.
Implementation Tasks
This deliverable has four parts; each part will be graded on its own rubric. You should complete the assignment one part at a time, in the order presented here.
Task 1: Implement Filtering by asked_by Field
The asked_by field in the questions schema represents the username of the user who asked the question, essentially identifying the author of the question. The objective of this task is to enhance the current functionality by adding the capability to filter questions based on the asked_by field. This will allow users to retrieve questions posted by a specific user. Make sure you follow TDD, so work your way up by making sure your code passes the tests in application.spec.ts.
Steps to Achieve This
-
Add the
filterQuestionsByAskedByfunction
Create a new function calledfilterQuestionsByAskedByin theapplication.tsfile. This function will accept a list of questions and the name of a user as arguments and filter the given list of questions, returning only those asked by the specified user. -
Update the
getQuestionsByFilterfunction
Modify thegetQuestionsByFilterfunction within the questions controller (question.ts) to incorporate the new filtering functionality based on theasked_byfield. This involves integrating thefilterQuestionsByAskedByfunction to ensure that the questions are filtered by the specified user before any other filtering operations.Hint: you may need to look into
FindQuestionRequestand make necessary changes. -
Testing the implementation
After implementing these changes, it’s crucial to thoroughly test the new functionality. Ensure that questions are correctly filtered by theasked_byfield and that the existing filtering mechanisms (by search keywords and tags) remain unaffected. To ensure accuracy in your implementation, please add additional tests toapplication.spec.tsandquestions.spec.tsand make sure that the code coverage is as comprehensive as possible for the chunks of code you have added or updated as part of this feature.
Grading for implementation tasks:
- Adding
filterQuestionsByAskedBy: 5 points - Updating
getQuestionsByFilter: 5 points - Testing: 3 points
Task 2: Enhancing the Tags Model by Adding a Description Field
The goal of this task is to enhance the existing Tags model by introducing a description field. Tags appear as attributes below questions, acting as labels or keywords used to organize and identify information.
For example, the question “How to navigate using React Router?” might have tags like “REACT” and “JAVASCRIPT” to emphasize the languages and frameworks used.
This new field will provide users with a descriptive overview of each tag, improving the user experience by clarifying the meaning of tags. For instance, a tag like “ROUTER” might have different meanings depending on the context, such as “a hardware device” or “a file to organize website navigation links.”
The following steps outline the modifications required in the server to accommodate this new field.
Steps to Achieve This
-
Update the
getTagsFunction
The currentgetTagsfunction inapplication.tsaccepts an array of tag objects, which is only defined to have_idandname. You will first need to changeTagto also includedescription.Then, this function needs to be modified to do the following:
- Remove duplicate tags, ensuring that if the incoming array of tag objects contains objects with the same name, only the first tag object is used and others are discarded.
- Check the database for existing tags.
- Create new tags if they do not already exist.
- Return the modified tags.
-
Create the
getTagByNameFunction and Endpoint
You need to create a new functiongetTagByNameinserver/controller/tag.ts. Its expected behavior can be found inserver/tests/newTags.spec.ts. You need to ensure that your implementation passes the tests.Hint: see
getQuestionByIdinserver/controller/question.tsandaddTaginapplication.tsfor how some of the behaviors can be achieved. -
Test the Implementation
To ensure the accuracy of your implementation, conduct the following tests:- Test the
getTagsfunction correctly handles the creation of new tags, removal of duplicates, and retrieval of existing tags. - Test the
getTagByNamefunction to ensure it accurately returns the correct tag data based on the provided name. Consider the case where it cannot find a tag given the name.
Your implementation needs to pass existing tests. If existing tests are not fully covering every case of your implementation, you need to add additional tests to achieve full coverage in the coverage report.
- Test the
Grading for implementation tasks:
- Update
getTags: 3 points - Create
getTagByName4 points - Testing: 3 points
Task 3: Implement Sorting by Most Views
As part of this task, you will be working on a function to retrieve questions based on their view count. You are provided with the getQuestionsByOrder function, which is currently designed to fetch questions from a database and sort them based on the specified order. The function currently supports fetching active, unanswered, and newest questions. Your task is to implement the logic for fetching the most viewed questions. Make sure you follow TDD, so work your way up by understanding and making sure your code passes the tests in application.spec.ts.
Steps to Achieve This
-
Add the
sortQuestionsByMostViewedFunction
Create a new function calledsortQuestionsByMostViewedin theapplication.tsfile. This function should take a list of questions as input and return the questions sorted by their view count in descending order. -
Update the
getQuestionsByOrderFunction
Modify thegetQuestionsByOrderfunction within the same file (application.ts) to incorporate the new sorting functionality. This involves utilizing the function implemented in Step 1. -
Testing the Implementation
After implementing these changes, it’s crucial to thoroughly test the new functionality. Ensure that questions are correctly sorted by most views, and that the existing sorting features (active, unanswered, and newest) remain unaffected. To ensure your implementation is accurate, please add tests inapplication.spec.tsand ensure the code coverage is as thorough as possible for the portions of code you have added or updated as part of this feature.
Grading for implementation tasks:
- Add
sortQuestionsByMostViewed: 5 points - Update
getQuestionsByOrder: 5 points - Testing: 3 points
Task 4: Implement Upvoting and Downvoting Functionality
Upvoting and downvoting features allow users to express their opinions on questions by adding or removing their votes. This functionality is crucial for a community-driven platform where user engagement and feedback are important. Make sure you follow TDD, so work your way up by understanding and making sure your code passes the tests in application.spec.ts and question.spec.ts.
Upvoting a Question
When a user upvotes a question, the following actions take place:
- Update Upvotes List: The user’s username is added to the
up_votesfield of the question. This field is an array that tracks all the users who have upvoted the question. - Remove Downvote (if present): If the user had previously downvoted the question, their username is removed from the
down_voteslist to prevent contradictory actions by the same user. - Success and Cancellation: If the user has already upvoted the question, their vote is cancelled, which involves removing their username from the
up_voteslist.
Downvoting a Question
Similarly, when a user downvotes a question:
- Update Downvotes List: The user’s username is added to the
down_votesfield of the question. This field is an array that records all the users who have downvoted the question. - Remove Upvote (if present): If the user had previously upvoted the question, their username is removed from the
up_voteslist. - Success and Cancellation: If the user has already downvoted the question, their vote is cancelled, which involves removing their username from the
down_voteslist.
Key Points
- Each question maintains two separate lists:
up_votesanddown_votes, which are updated based on user interactions. - Users can toggle their vote on a question, which means they can switch from upvoting to downvoting or vice versa.
- Proper error handling ensures that issues like missing fields in requests or database errors are managed appropriately, providing a smooth user experience.
Steps to Achieve This
-
Add Upvote and Downvote Functions
Implement two functions,addUpvoteToQuestionandaddDownvoteToQuestion, inserver/models/application.tsto handle upvoting and downvoting of questions. These functions will:- Check if the question exists.
- Add or remove the user’s vote (upvote or downvote) as appropriate.
- Update the question’s upvote and downvote counts.
-
Update Routes to Handle Voting
Add two new routes,"/upvoteQuestion"and"/downvoteQuestion", inserver/controller/question.tsto handle upvote and downvote requests. These routes will use the newly created functions to update the question’s votes. -
Test the Voting Functionality
To verify the behavior of the upvote and downvote features, make sure your code passes the tests inapplication.spec.tsandquestion.spec.tsfiles. For your reference, test the following functionalities:- Successful upvoting and downvoting.
- Cancelling an upvote or downvote.
- Handling edge cases such as missing parameters in requests. Specifically, ensure the functionality handles scenarios where a user who previously upvoted now intends to downvote. The expected behavior in this case is that the user should be removed from the
up_votesarray and added to thedown_votesarray. Additionally, consider the reverse scenario where a user who previously downvoted now intends to upvote.
Ensure that the code coverage is as thorough as possible for the portions of code you have added or updated as part of this feature.
Grading for implementation tasks:
addUpvoteToQuestionandaddDownvoteToQuestion: 30 points- Updating routes: 20 points
- Testing: 4 points
Submission Instructions & Grading
You will submit your assignment using GitHub Classroom.
This submission will be scored out of 100 points, 90 of which will be awarded for implementation of tasks and accompanying tests, and the remaining 10 for following style guidelines.
Testing
You will be provided with starter code that includes a set of tests. Your task is to ensure that all existing tests pass and to create additional tests to cover any new functionality or edge cases.
Your code will be evaluated for linting errors and warnings. Submissions that have any linter errors will automatically receive a grade of 0. Do not wait to run the linter until the last minute. To check for linter errors, run the command npm run lint from the terminal. The handout contains the same ESlint configuration that is used by our grading script.
Manual Grading
Your code will be manually evaluated for conformance to our course style guide. This manual evaluation will account for 10% of your total grade on this assignment. We will manually evaluate your code for style on the following rubric:
To receive all 10 points:
- All new names (e.g. for local variables, methods, and properties) follow the naming conventions defined in our style guide
- There are no unused local variables
- All public properties and methods (other than getters, setters, and constructors) are documented with JSDoc-style comments that describe what the property/method does, as defined in our style guide
- The code and tests that you write generally follows the design principles discussed in week one. In particular, your design does not have duplicated code that could have been refactored into a shared method.
We will review your code and note each violation of this rubric. We will deduct two points for each violation, up to a maximum of deducting all 10 style points.
Debugging :
If you need help troubleshooting a problem, be sure to follow all the steps outlined in the course’s debugging policy. This will ensure you have exhausted all initial debugging strategies before reaching out for assistance from the TAs.